Podalia Ancient City Magnificent Remnants of Prehistoric Anatolia
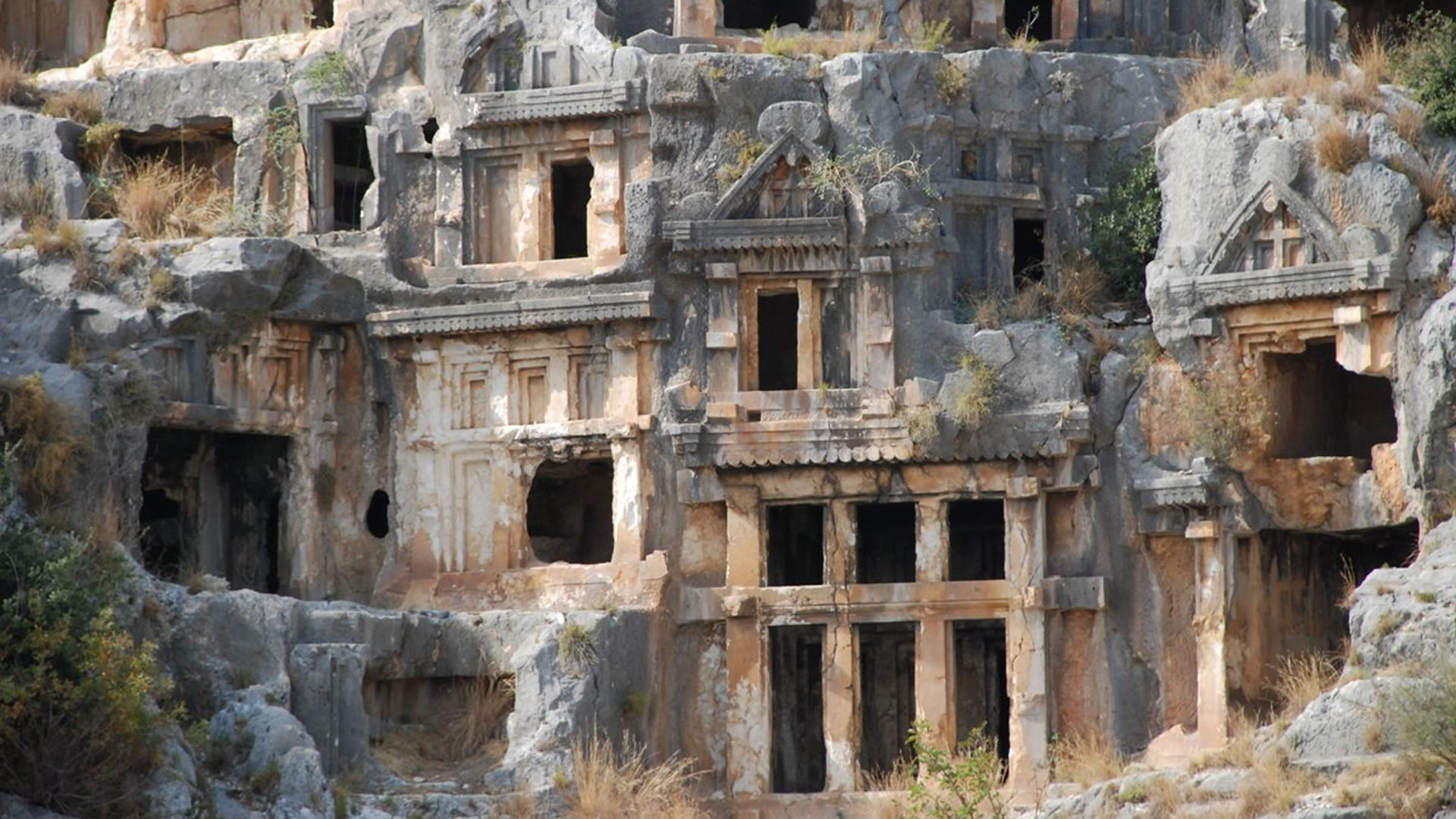

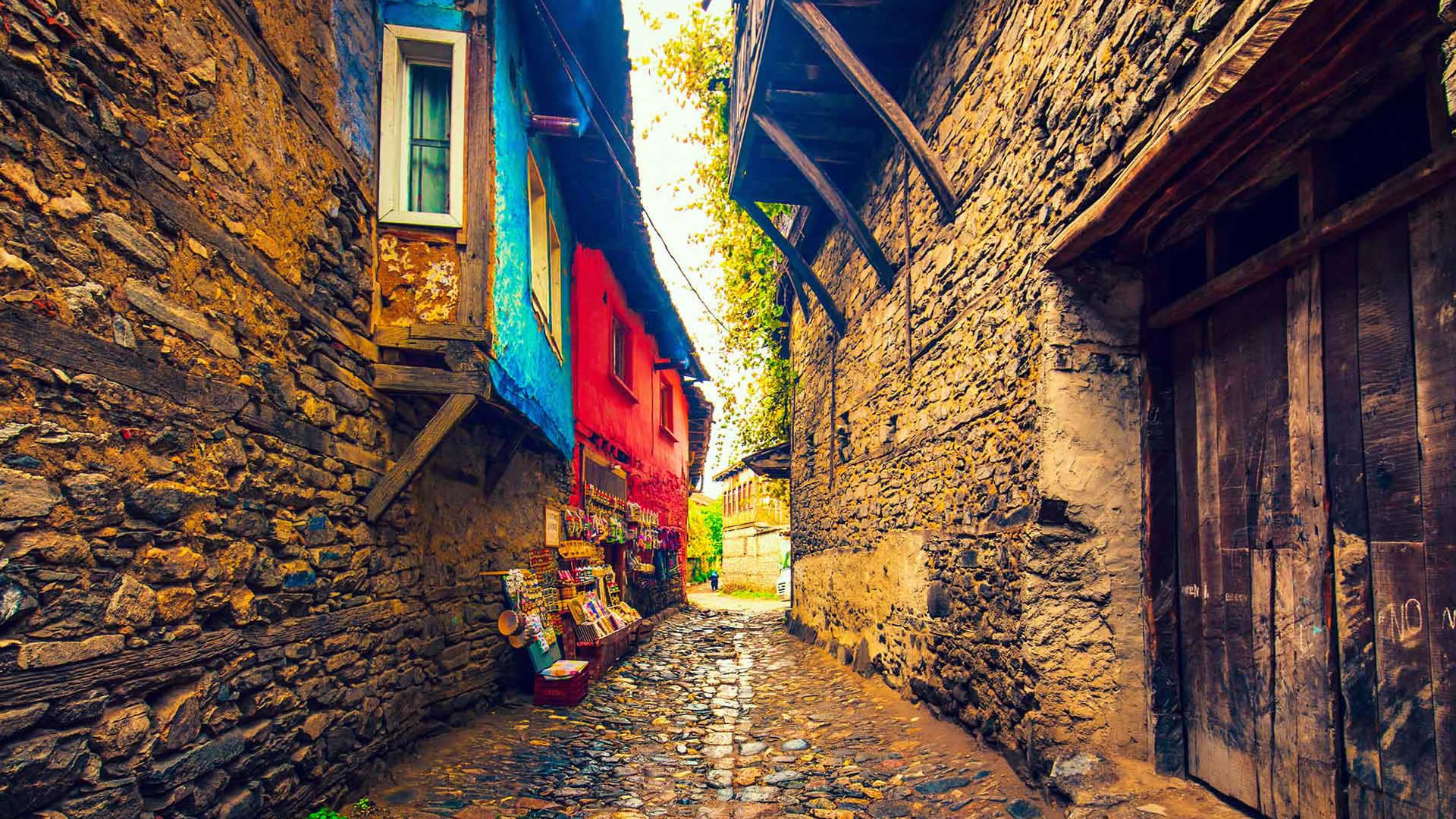
Anatolia boasts numerous ancient cities that shed light on its rich history. One such site is the Podalia Ancient City, renowned for its splendid remnants and historical significance, capturing the attention of archaeologists and history enthusiasts alike.
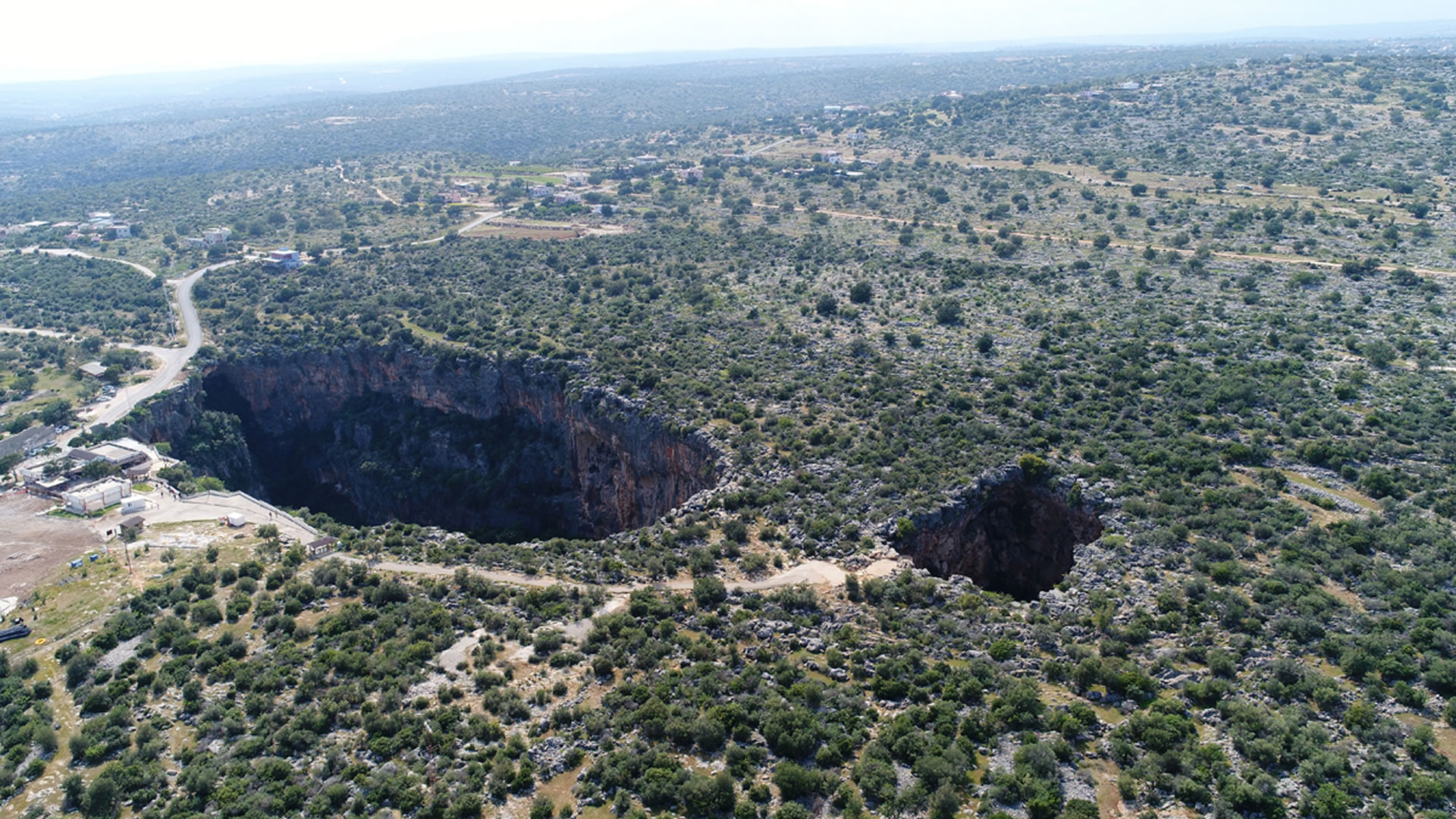
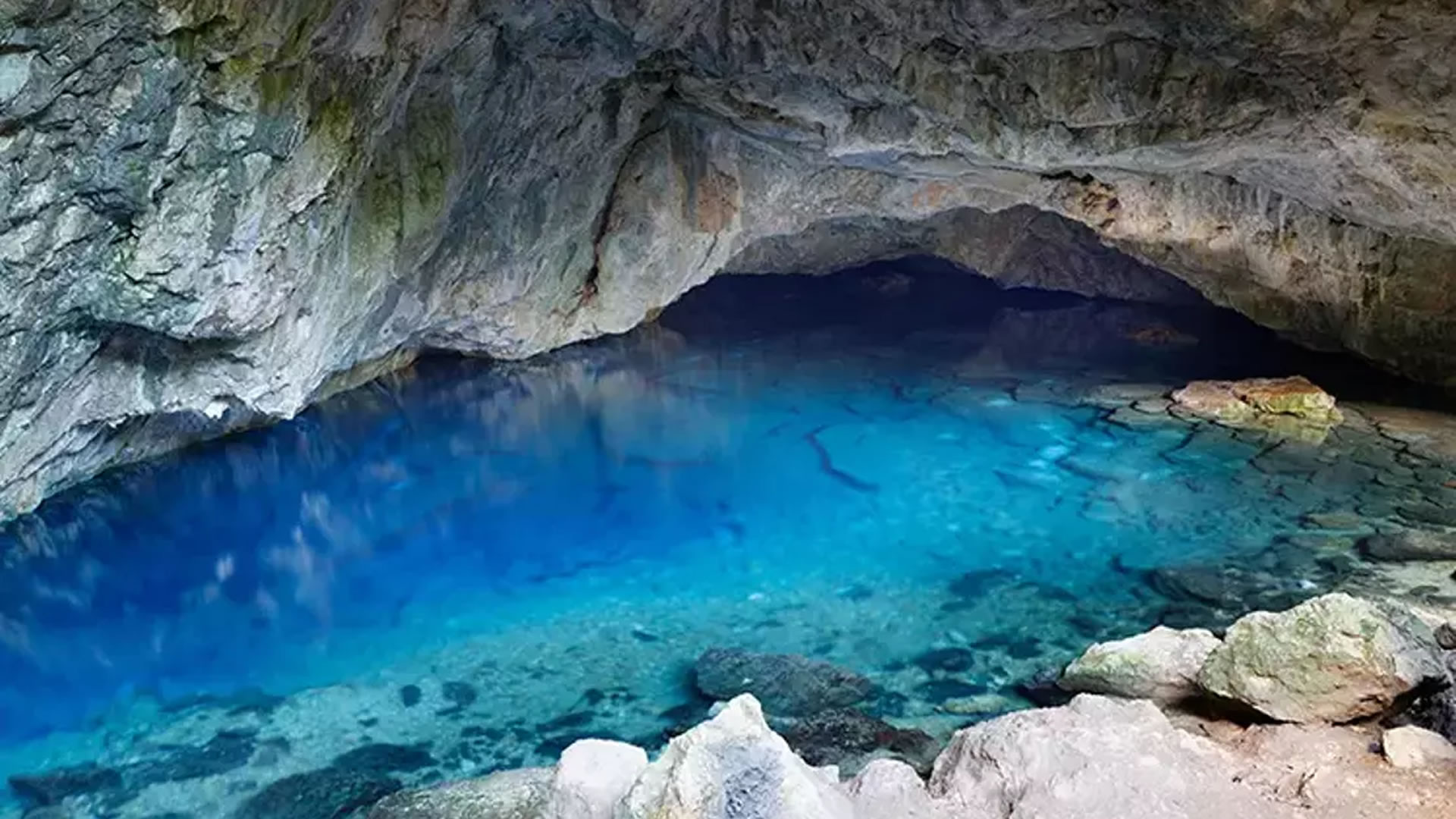
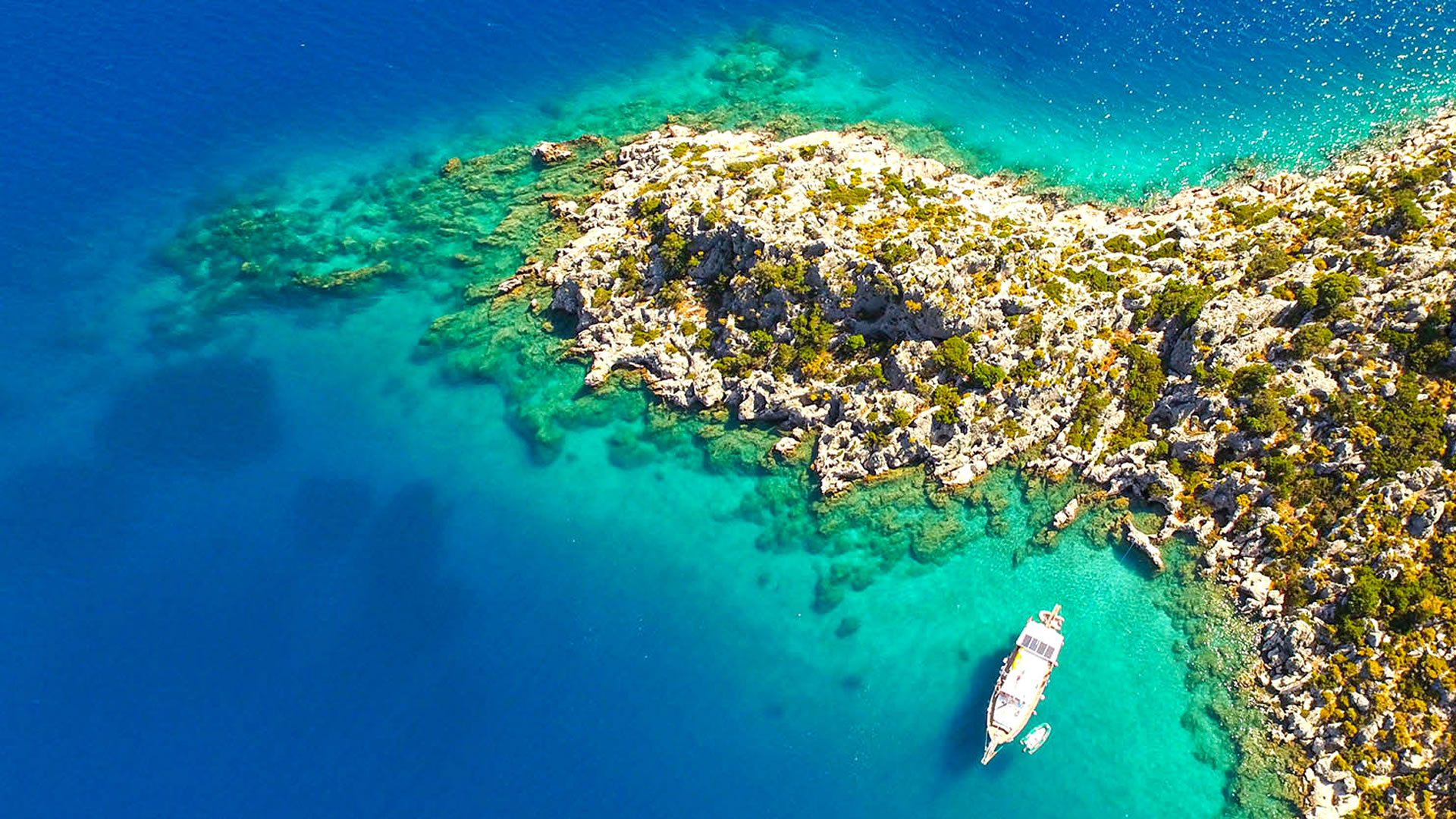
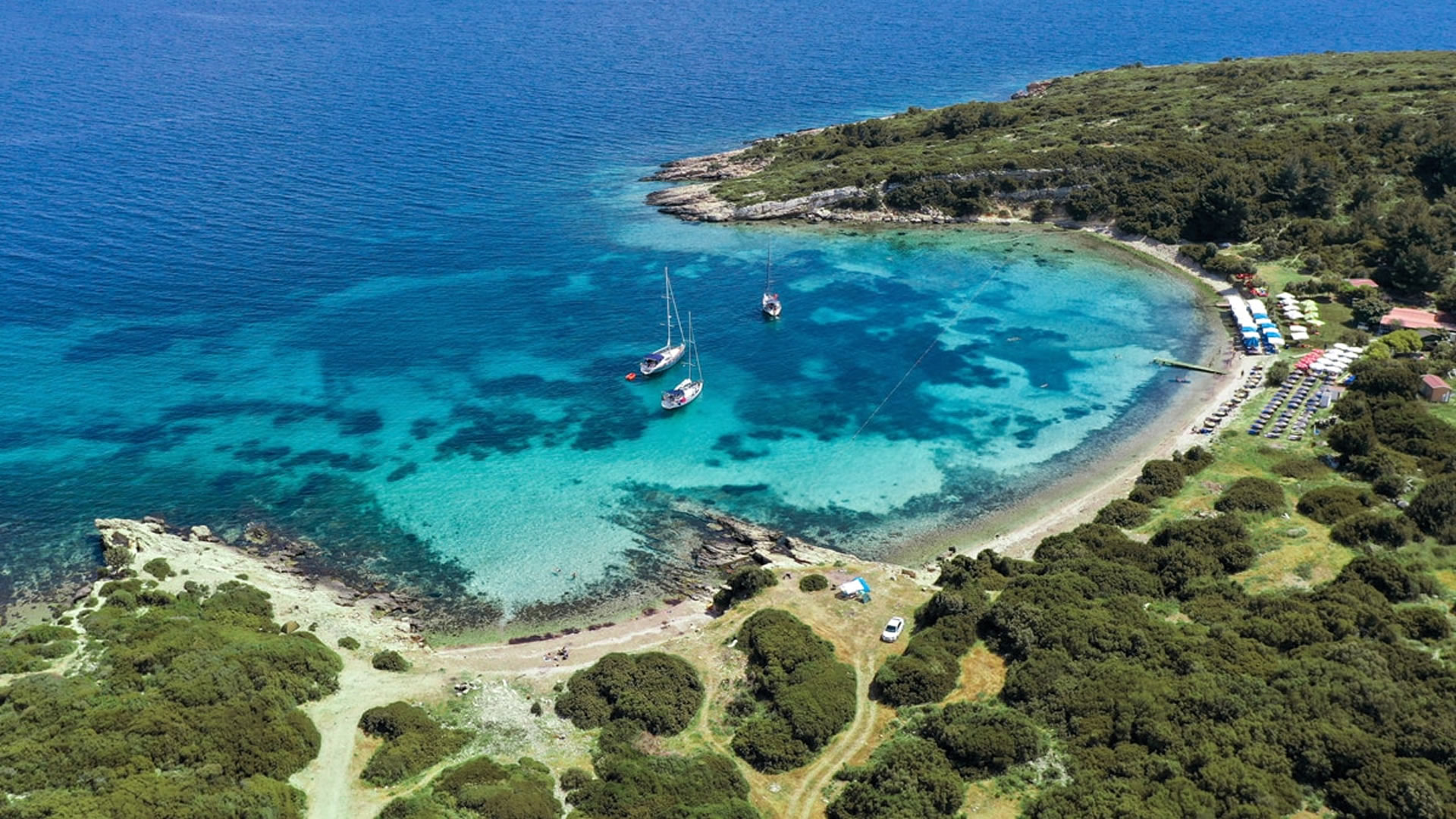
Podalia Ancient City is recognized as an archaeological site located within the modern borders of Turkey. While the precise location of the ancient city remains to be definitively determined, it is generally believed to have been situated in the western regions of Anatolia, within the Aegean Region. The history of Podalia dates back to the middle of the 2nd millennium BCE, establishing it as a significant settlement during that era.
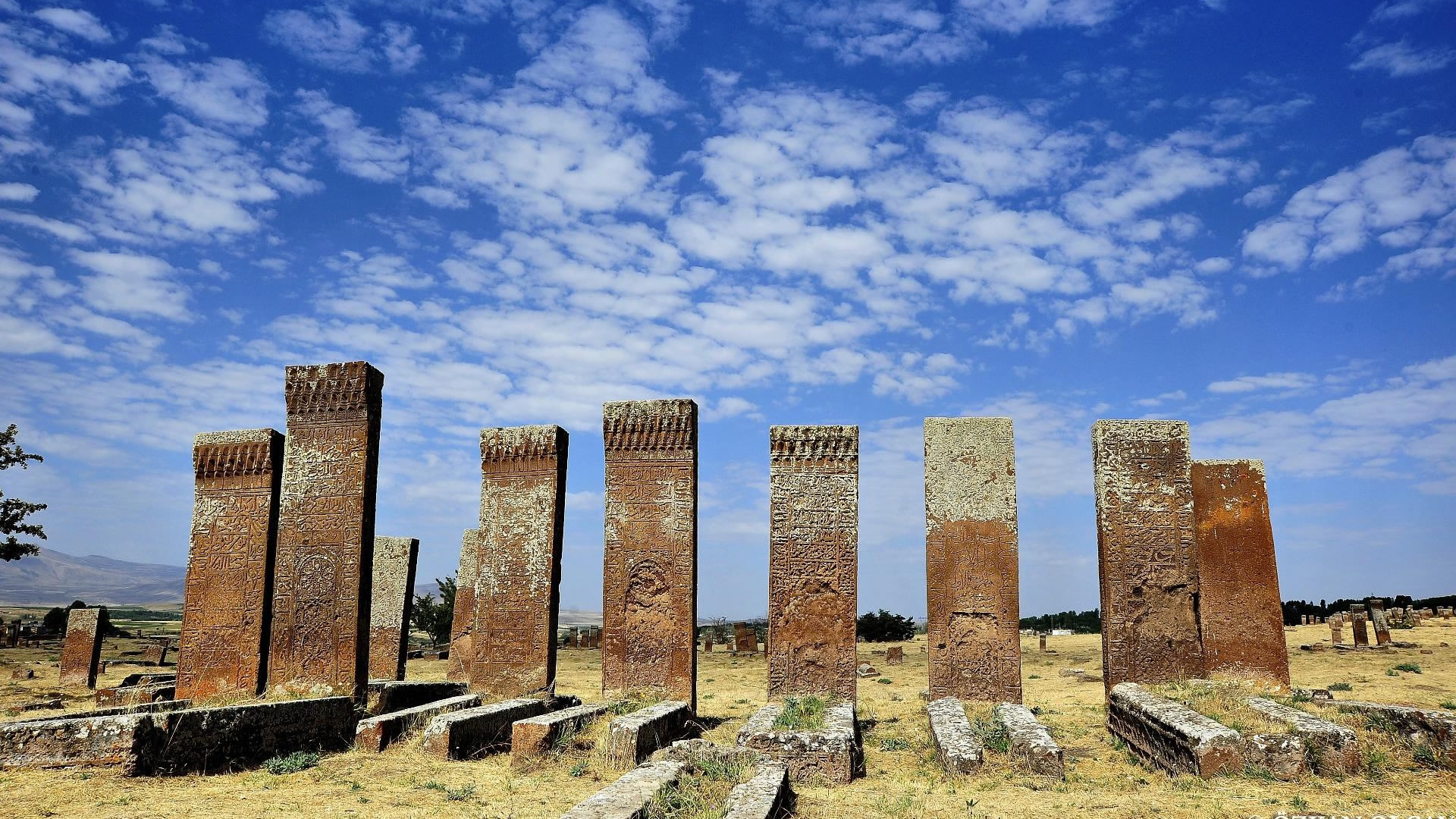
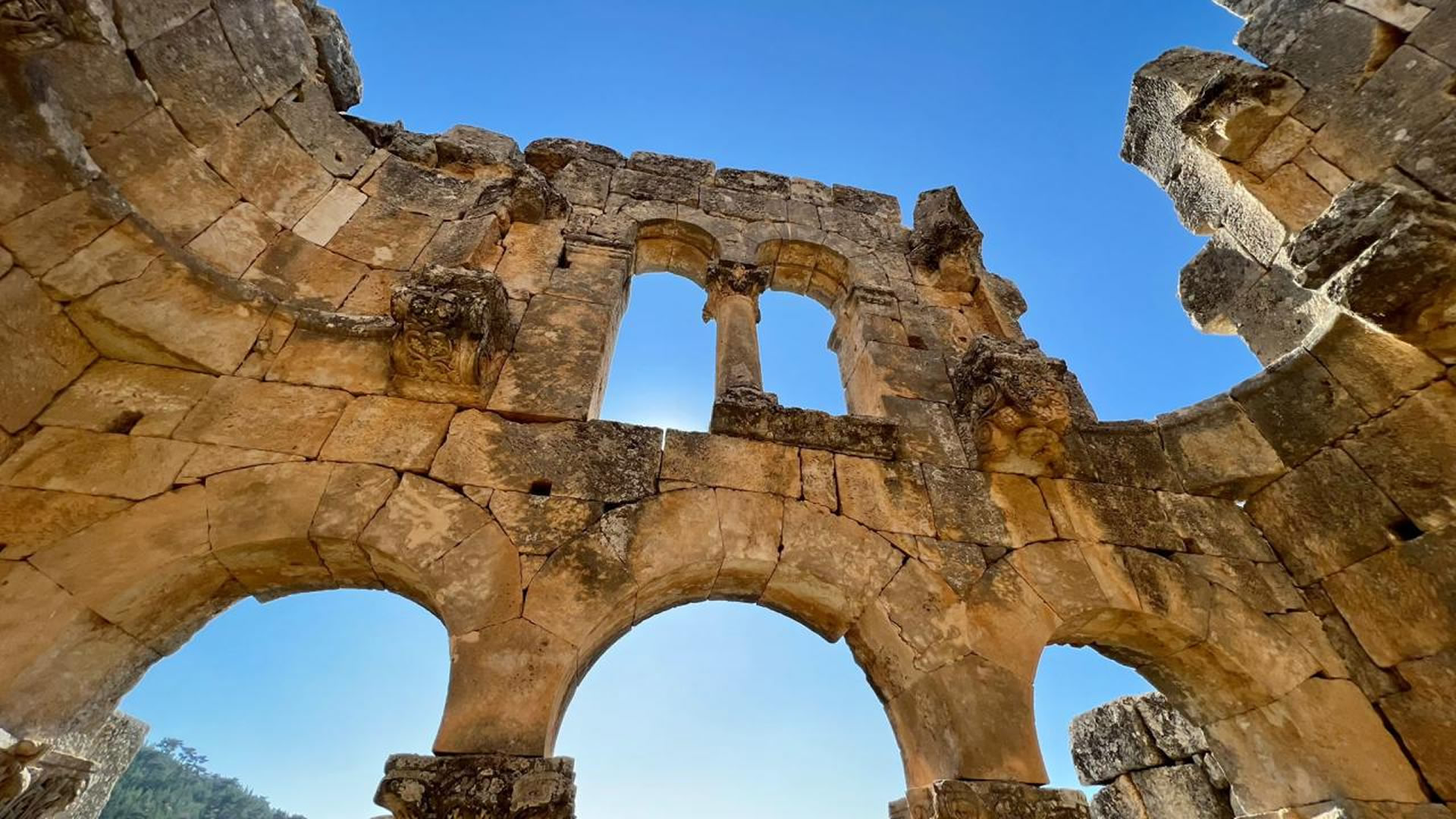
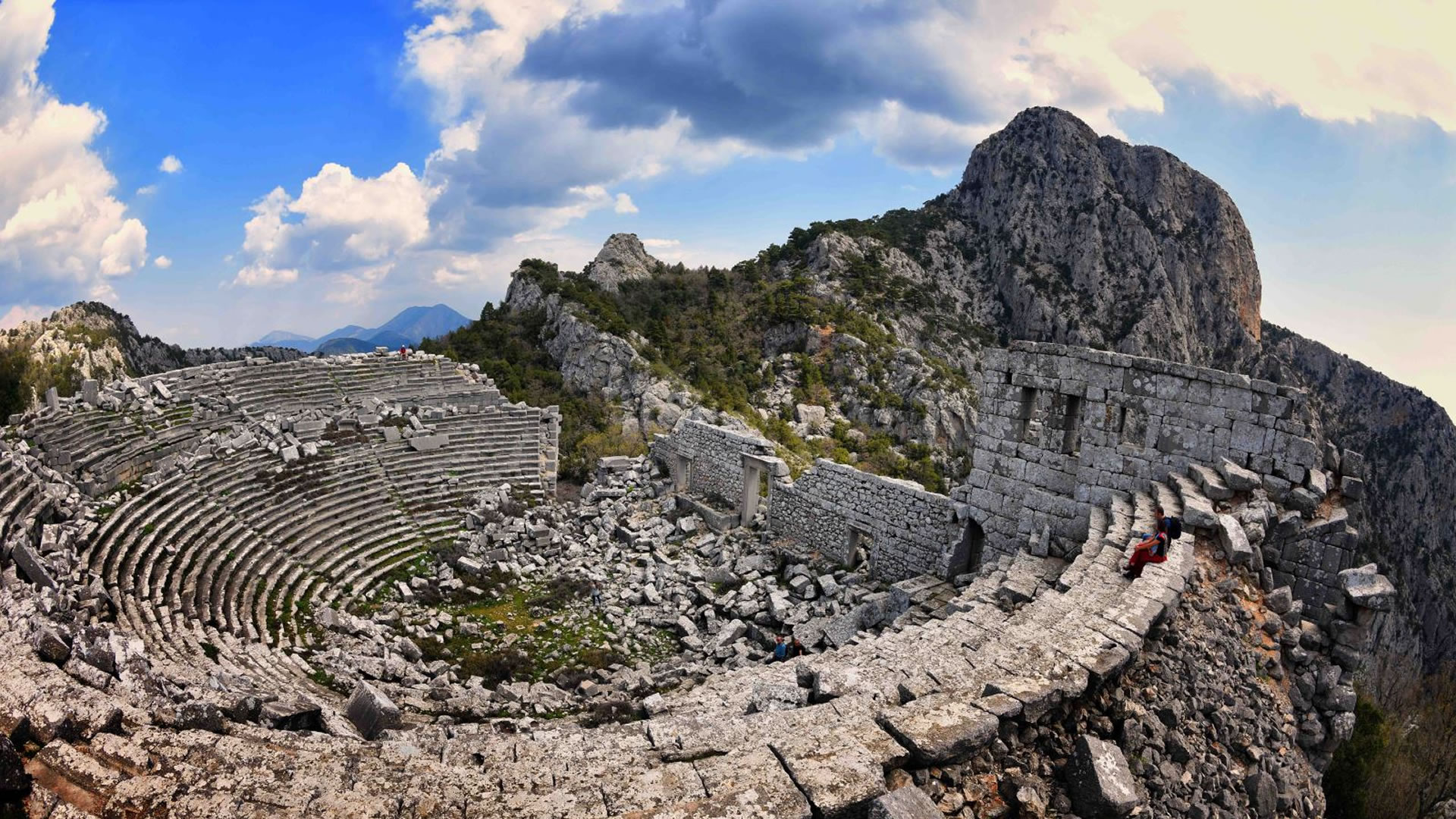
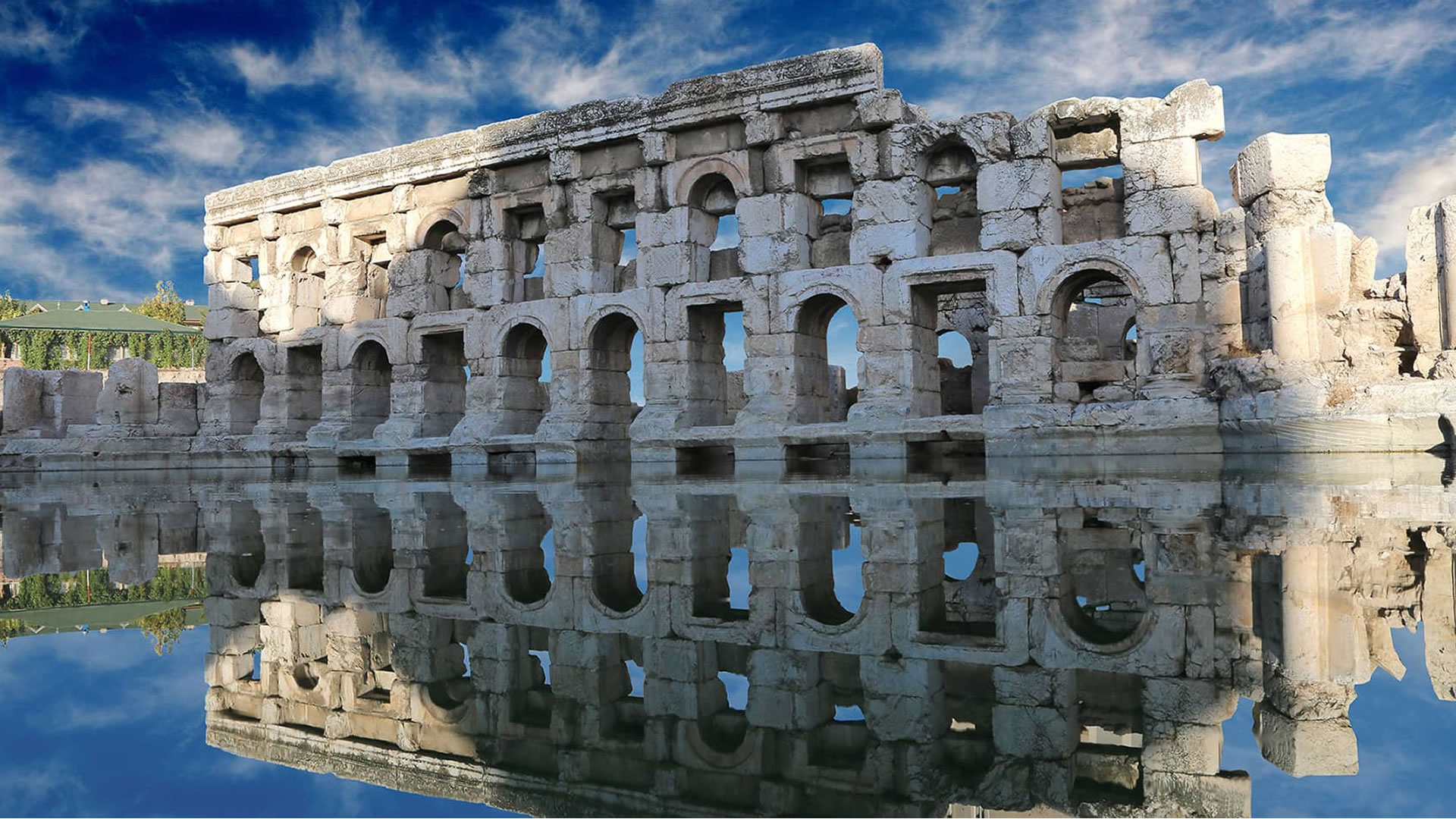
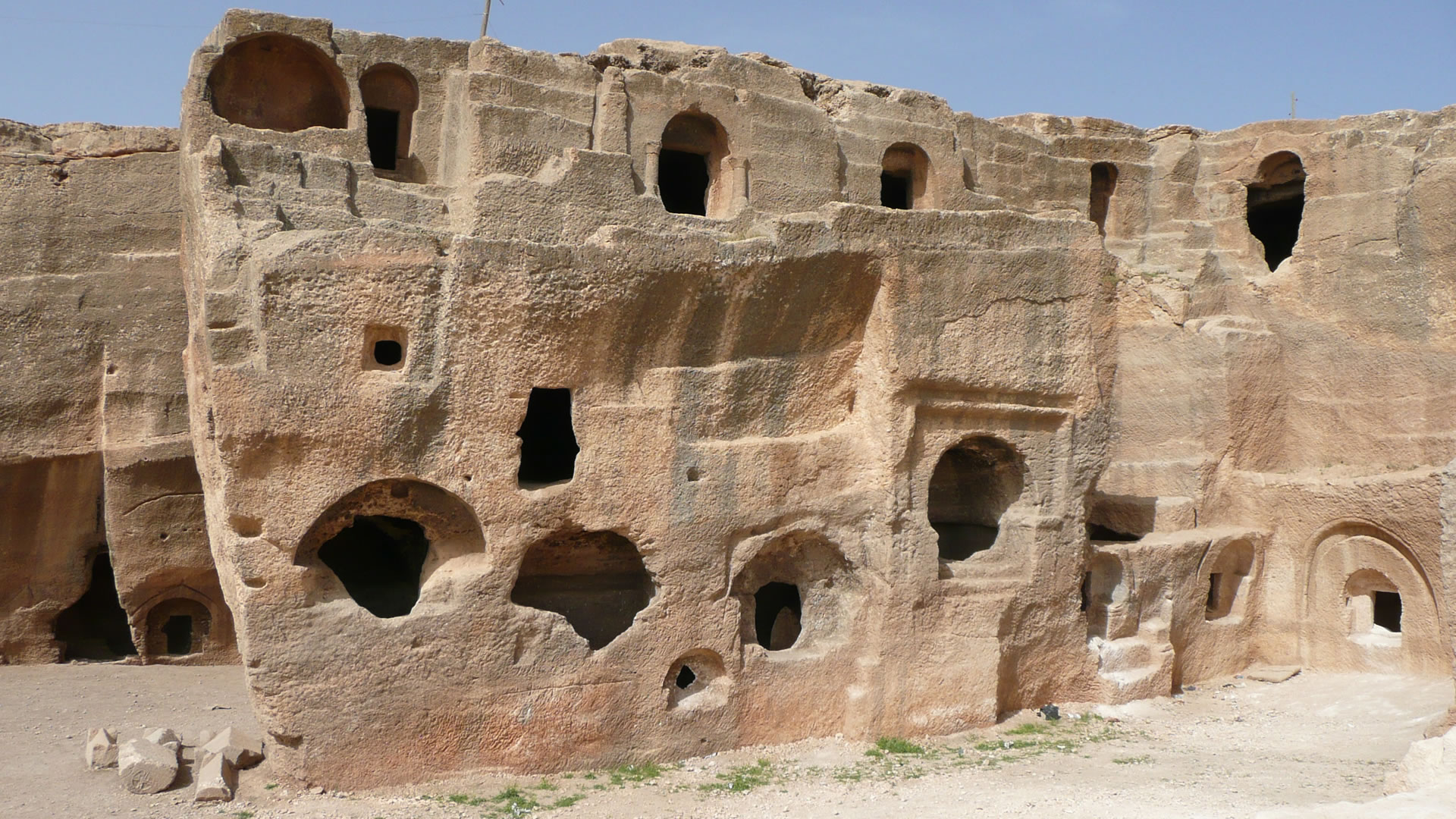
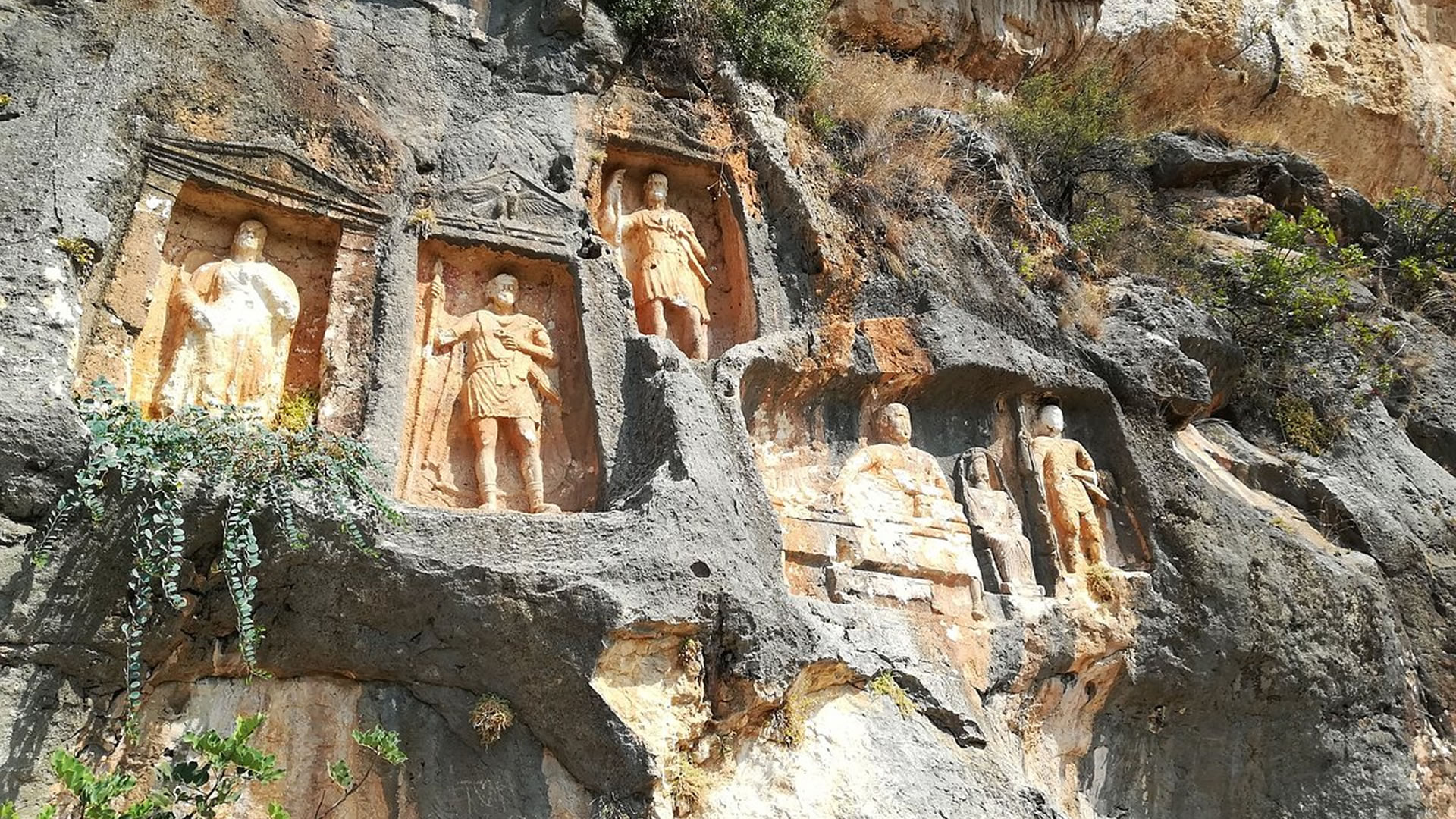
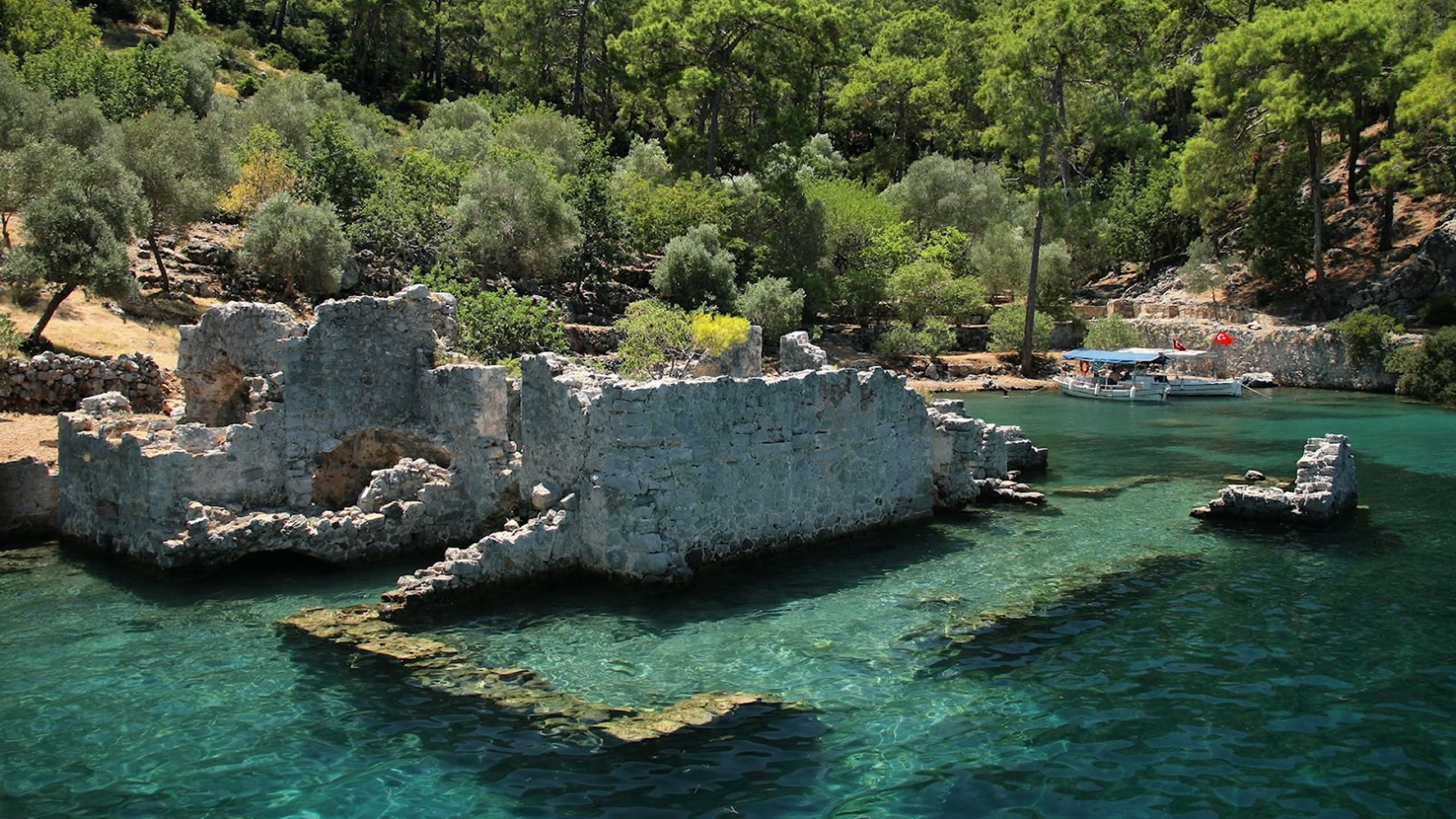
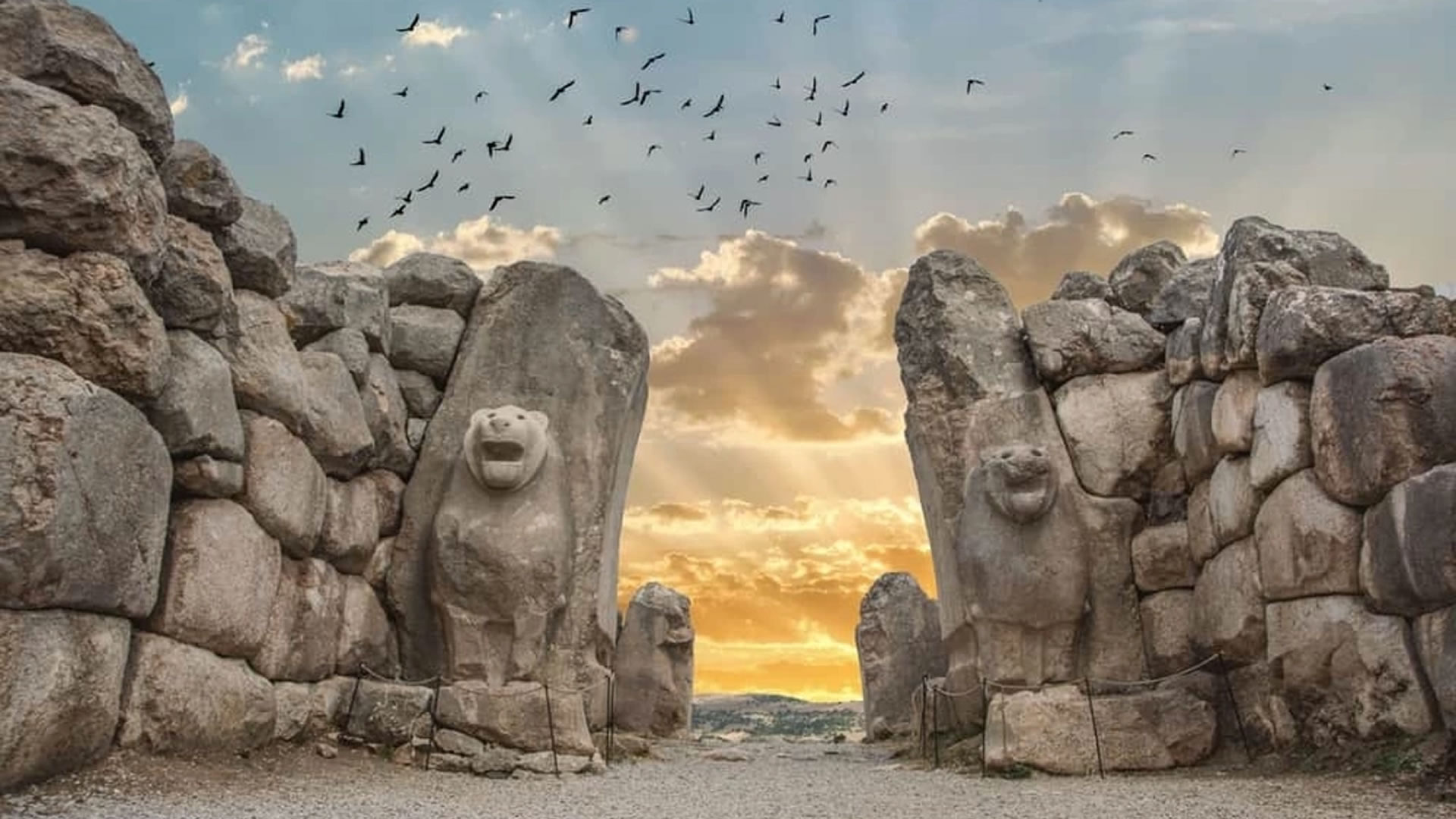
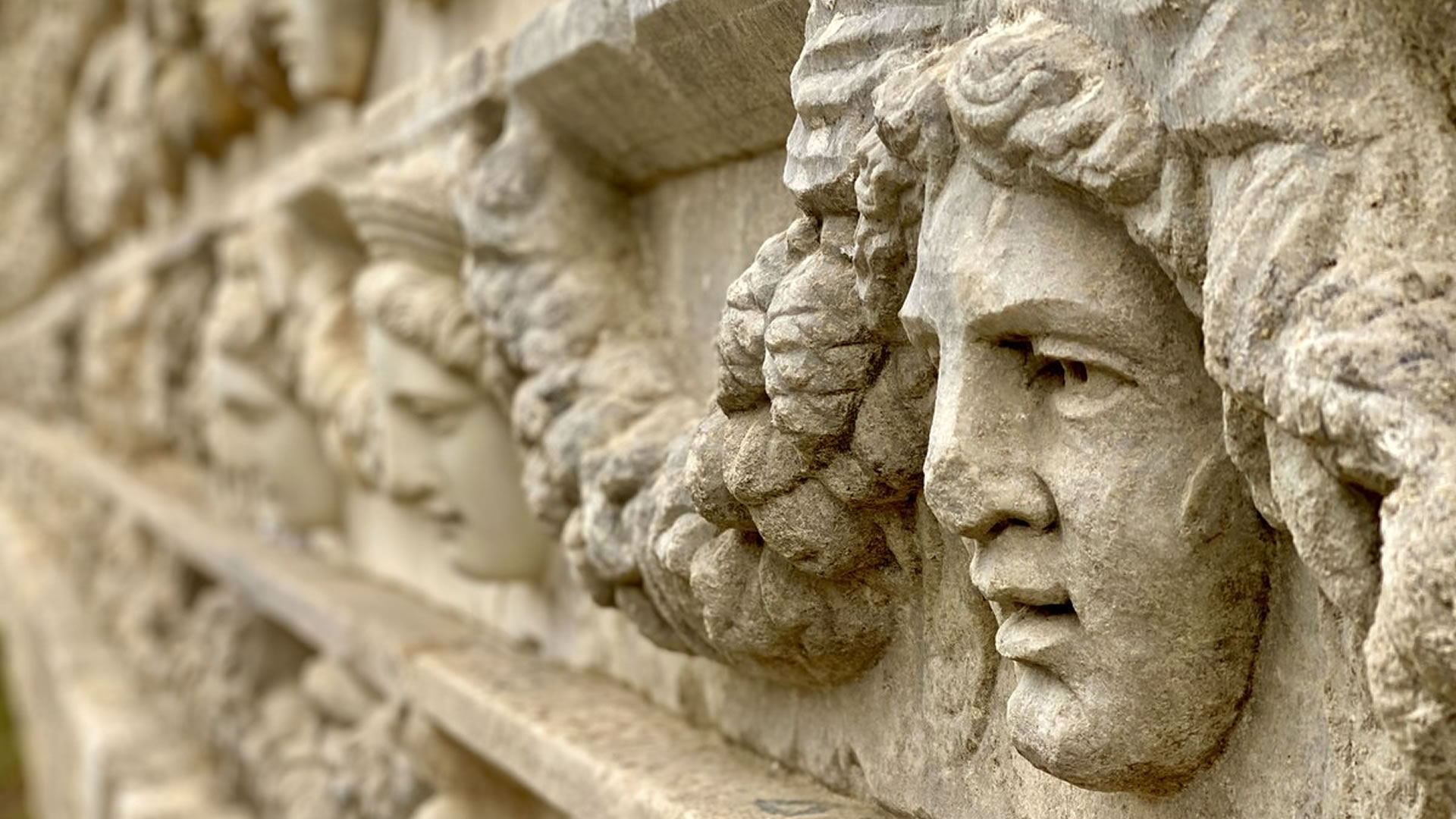
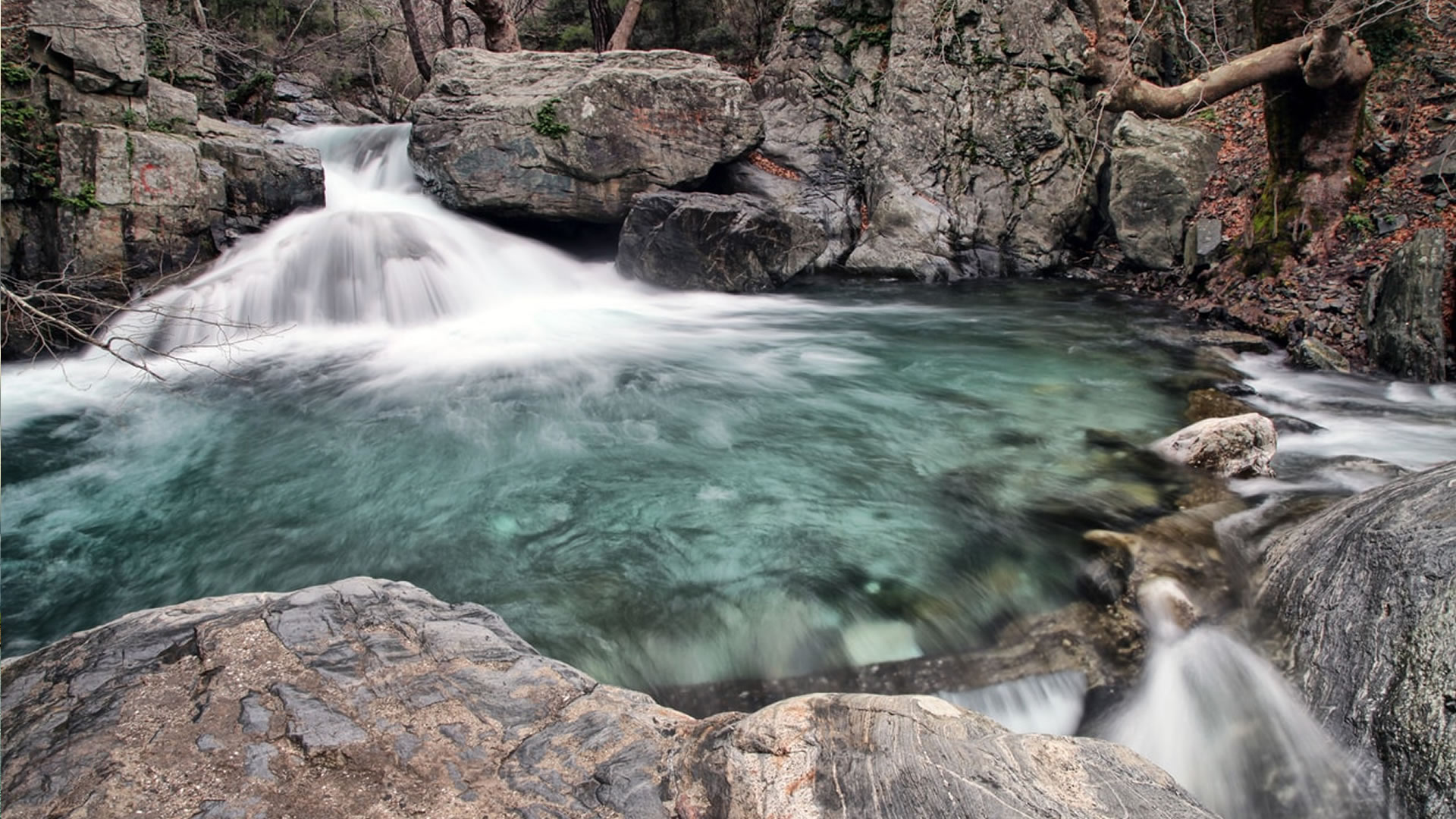
Podalia stands out for its architectural structure and remnants. The archaeological findings within the ancient city reveal traces spanning various periods. Excavations unearthed remnants including temples, palaces, walls, necropolis areas, and commercial centers.
Temples in Podalia served as places where religious rituals were conducted during ancient times. Typically situated at the heart of the city, these temples were dedicated to various deities. The city walls signify Podalia's strategic positioning and defensive purposes. Remains of palaces offer insights into the administrative and governmental structures of the ancient era.
Archaeological endeavors in Podalia also shed light on the daily lives of its inhabitants. Commercial centers and marketplaces discovered within the city indicate the vibrancy of its economic activities. Additionally, agricultural fields and water sources surrounding Podalia underscore the importance of agricultural practices during antiquity.
Podalia Ancient City forms a vital part of Anatolia's prehistoric heritage. Its historical and architectural remnants provide valuable insights into life during ancient Anatolia. Furthermore, Podalia serves as a significant resource for understanding the historical and cultural background of its surrounding region.
The discovery and exploration of Podalia have contributed significantly to the field of archaeology. Excavations conducted within the ancient city have enhanced our understanding of the social, economic, and religious structures of ancient Anatolia. Moreover, the findings in Podalia have expanded our knowledge of the settlement history of the region during prehistoric and ancient times.
Podalia Ancient City stands as a testament to Anatolia's rich historical legacy. With its magnificent architectural remnants and historical significance, it continues to be a focal point for research and exploration among archaeologists and history enthusiasts. The history and remnants of Podalia shed light on the ancient periods of Anatolia, facilitating a better understanding of the region's past.
Further research and conservation efforts in Podalia will contribute to the expansion of knowledge regarding Anatolia's ancient history and ensure the preservation of this invaluable heritage for future generations.
Podalia Ancient City is recognized as an archaeological site located within the modern borders of Turkey. While the precise location of the ancient city remains to be definitively determined, it is generally believed to have been situated in the western regions of Anatolia, within the Aegean Region. The history of Podalia dates back to the middle of the 2nd millennium BCE, establishing it as a significant settlement during that era.
Podalia stands out for its architectural structure and remnants. The archaeological findings within the ancient city reveal traces spanning various periods. Excavations unearthed remnants including temples, palaces, walls, necropolis areas, and commercial centers.
Temples in Podalia served as places where religious rituals were conducted during ancient times. Typically situated at the heart of the city, these temples were dedicated to various deities. The city walls signify Podalia's strategic positioning and defensive purposes. Remains of palaces offer insights into the administrative and governmental structures of the ancient era.
Archaeological endeavors in Podalia also shed light on the daily lives of its inhabitants. Commercial centers and marketplaces discovered within the city indicate the vibrancy of its economic activities. Additionally, agricultural fields and water sources surrounding Podalia underscore the importance of agricultural practices during antiquity.
Podalia Ancient City forms a vital part of Anatolia's prehistoric heritage. Its historical and architectural remnants provide valuable insights into life during ancient Anatolia. Furthermore, Podalia serves as a significant resource for understanding the historical and cultural background of its surrounding region.
The discovery and exploration of Podalia have contributed significantly to the field of archaeology. Excavations conducted within the ancient city have enhanced our understanding of the social, economic, and religious structures of ancient Anatolia. Moreover, the findings in Podalia have expanded our knowledge of the settlement history of the region during prehistoric and ancient times.
Podalia Ancient City stands as a testament to Anatolia's rich historical legacy. With its magnificent architectural remnants and historical significance, it continues to be a focal point for research and exploration among archaeologists and history enthusiasts. The history and remnants of Podalia shed light on the ancient periods of Anatolia, facilitating a better understanding of the region's past.
Further research and conservation efforts in Podalia will contribute to the expansion of knowledge regarding Anatolia's ancient history and ensure the preservation of this invaluable heritage for future generations.